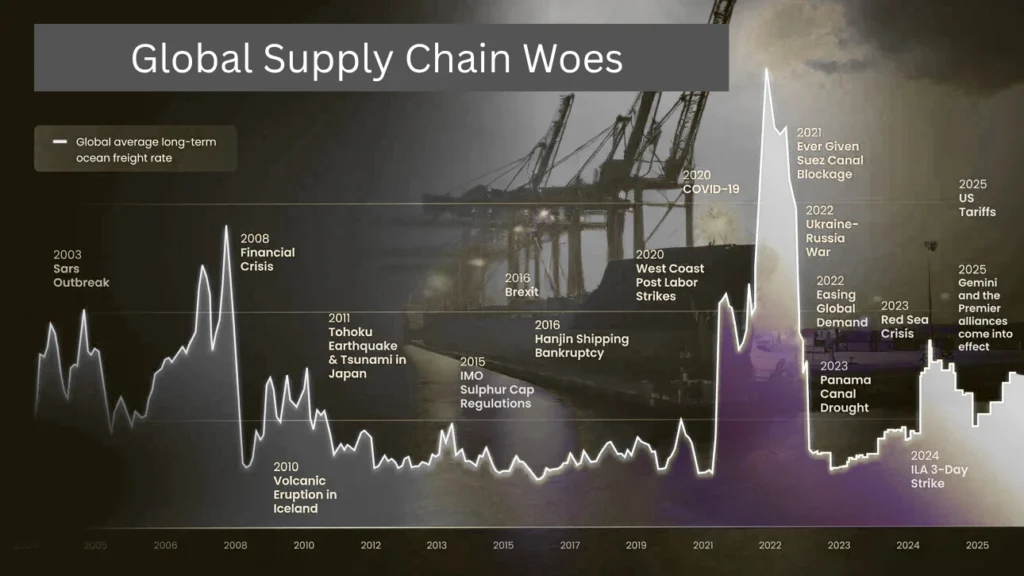
The Global Supply Chain Woes, interference continues to recover since the COVID-19 pandemic disruptions, and in 2025, businesses and consumers continue to face shortages, delays, and rising costs.

This includes advancing impact from instability in geopolitics, pandemic, and expanded demand, all aggravated by the shortage of labor, cost rise to environmental interests. From shipping bottlenecks to geopolitical tensions, multiple factors are donating to the ongoing crisis.
In this article, we’ll explore the key reasons behind persistent supply chain disruptions, examine recent events affecting global trade, and discuss what businesses and consumers can expect in the coming months with a survey report for 2025.

Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Key Causes & Impacts (2025)
According to the survey, the top contributors to supply chain instability include pandemic-related interruptions, unstable geopolitics, rising costs with increased demand, and climate and environmental issues.
| Global Supply Chain Woes -Chain Disruptions | |||
| Category | Key Factors | Impact on Supply Chains | Industries Most Affected |
| Pandemic Disruptions | Shifting Consumer Demand | surge-electronics/home goods.Decline-travel/entertainment. | Retail/E-commerce/ Logistics |
| Labor Shortages | Reduced staff in shipping and warehousing. | Manufacturing, Trucking, Retail | |
| Production &Transportation | Factory shutdowns, port congestion, and delayed shipping | Automotive/Electronics/Consumer Goods | |
| Inventory Imbalances | Overstock of some goods, shortages of others due to demand fluctuations. | Retail/Pharmaceuticals/Food & Beverage | |
Geopolitical Instability | Trade Wars & Tariffs | Higher costs, restricted trade flows, and supply shortages. | Electronics/Automotive/Agriculture |
| Political Unrest & Conflicts | Flutter production, blocked trade routes. | Energy, Agriculture, Manufacturing | |
| Sanctions | Limited access to critical materials | Tech/Energy/Aerospace | |
Increased Demand | Pent-up Demand | Post-pandemic spending surge strains supply chains. | Retail/Automotive/ Travel |
| Rising Freight Costs | Shipping rates remain high | Logistics/Import/Export Businesses | |
| Material Scarcity | Shortages of semiconductors/ metals, and plastics slow production. | Tech/Automotive/Construction | |
| Inflation | Higher production and logistics costs are passed to consumers. | All sectors | |
Climate & Environmental Issues | Extreme Weather Events | Hurricanes, floods, and droughts disrupt shipping and farming. | Agriculture, Energy, Construction |
| Resource Scarcity | Water shortages, deforestation, and mining | Food /Electronics / Textiles | |
Other Factors | Cybersecurity Threats | Ransomware attacks on ports/factories cause delays. | Logistics/Healthcare, Finance |
| Increased Consumer Expectations | Demand for fast shipping strains last-mile delivery networks. | E-commerce, Retail | |
| Lack of Skilled Workforce | Shortages of truckers, engineers, and technicians slow operations. | Transportation/Manufacturing/Tech | |
Note:

- Exports of grain and metals are affected by the Ukraine war
- due to fuel costs and port delays. Shipping rates remain high.
- Water shortages, deforestation, and mining challenges limit raw materials.
Distribution of the Global Supply Chain Woes and Impact on 2025
In the era of 2025, Global Supply Chain Woes to continue to impact and face major difficulties, but there’s also real progress being made. Here’s what’s shaping the aspects. Challenges like geopolitical tension, pressure of climate change, and labour shortage are the real problems.
Geopolitical Tensions Continue to Disrupt Trade
The ongoing wars in the world, like the Russia-Ukraine war, U.S.-China trade disputes, and instability in the Middle East, have drastically influenced global trade routes. Sanctions were imposed to ban exports, and shifting associations forced companies to rethink their supply chains.

Impact Areas:
- Electronics: faced export restrictions on Rare earth metals used in chips and batteries
- Energy: higher shipping costs for Oil and gas supply fluctuations
- Automotive: Sanctions on Russian metals mostly affected car manufacturing.
“Many companies are shifting to ‘friend-shoring’ sourcing from politically stable allies – but this transition takes time and investment,” says logistics analyst Maria Chen.
Labor Shortages: A Persistent Problem
In spite of promoting automation, many industries still struggle with manpower gaps. Younger workers aren’t entering logistics at the same rate as retirees leaving. The survey found:
- Manufacturing: Aging manpower & lack of skilled labor equals slower production.
- Shipping & Trucking: High turnover and demanding conditions lead to delays.
- Retail: Shortage of storehouse staff slows down the order fulfillment.
Notes:
Supply chain expert David Kwon. “Companies are raising wages, but it’s not enough to fill the gap.”
Climate Change & Extreme Weather Events
From hurricanes reducing ports to scarcity affecting the production of raw materials, the worsening of climate-related issues.
- Agriculture: Droughts in Europe and floods in Asia impact food supply chains.
- Construction: Extreme weather delays affect infrastructure projects.
- Energy: factories are affected by Heatwaves strain power grids.
“Companies that don’t factor climate risks into their supply chains will keep facing disruptions,” warns sustainability consultant Elena Rodriguez.
Rising Fuel & Transportation Costs
Electric trucks and alternative fuels are increasing as most logistics depend on diesel, because there is an Unpredictable high oil price, which is a major concern.
Impact:
- From 2024, Air freight costs up 18%.
- Trucking rates endure at 12% higher than pre-pandemic levels.
“Every dollar increase in oil prices trickles down to consumer prices,” says economist Raj Patel.
Semiconductor & Chip Shortages Still Linger
Even so, better from 2021-2023, the shortage of chips persists due to:
- High demand for AI, EVs, and smart devices
- Outside Taiwan & South Korea, there is a Limited production capacity
“For some chips, Automakers are still waiting for 6+ months,” reports tech analyst Liam Foster.
Over-reliance on Single Suppliers
Relying on one supplier or country is risky; many companies have learned not to do this, yet diversion is slow due to:
- The higher the costs of switching suppliers.
- Long-term contracts with existing partners.
“Dual-sourcing is the future, but it’s expensive,” admits procurement specialist Hannah Lee.
Port Congestion & Shipping Delays in 2025
While not critical as during COVID, bottlenecks still occur due to:
- Unloading delays due to Larger ships
- Labor strikes at major ports, e.g., recent disruptions in Germany & LA
Potential Risks for Future Supply Chain Problems
Several factors could cause more supply chain delays and shortages shortly:
- U.S. Port Obstruction Could Return: If shipping volumes spike again, American ports might face backlogs like the previous year.
- Russia-Ukraine War Impact on European Ports: Northern European shipping hubs could see disturbances due to the ongoing conflict.
- Air Cargo Limits (Asia-Europe Routes): Reduced air cargo capacity may weaken high-priority shipments between Asia and Europe.
- New COVID Lockdowns in China: If China restores strict pandemic measures, factory and port slowdowns could ripple globally.
- Rail Freight Disruptions (China-Europe Route): Problems on the onshore rail network between China and Europe may force more dependency on slower ocean shipping.
If not managed carefully, these risks could lead to higher costs, longer wait times, and product shortages. Businesses should monitor the issues more closely and investigate other shipping options if possible.
| Home | https://aiis.org/ |
Conclusion:
Will Supply Chains Ever Be Balanced?
- While some development has been made since the pandemic, the survey in 2025 shows that the supply chains are still fragile.
- Geopolitical risks, labor gaps, and climate change are long-term challenges requiring systemic changes.
- Businesses that invest in durability, diversification, and technology are far better.
- For consumers, price fluctuations and occasional shortages continue, especially for electronics, cars, and seasonal goods.






